Fin Fan Cooler Manufacturer and Supplier
What is a Fin Fan Cooler?
A Fin Fan Cooler, also known as an air cooler, is a cooling device developed in the 1940s that uses air to cool process fluids within pipes.
It has now largely replaced traditional water coolers. Fin Fan Coolers have become an indispensable component of cooling systems in refineries and petrochemical plants. Their applications range from overhead oil and gas condensation to gasoline and diesel cooling. Fin Fan Coolers are also widely used in the chemical, power, metallurgical, and atomic energy industries.

Fin Fan Cooler Classification
Fin fan cooler structures are generally categorized by process flow, structural form, air volume control method, ventilation method, and cold and frost protection.
1. Classification by Process Flow
a. Fin Fan Cooler with Front-end Dry Air Cooling, Rear-end Water Cooling
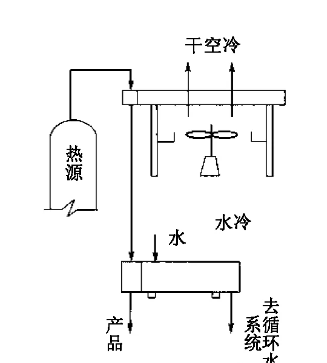
Applications and Features: Adequate water supply; Cooling medium outlet temperature must be close to the atmospheric wet-bulb temperature; Compact installation space.
Disadvantages: Requires a separate circulating cooling water system; High operating, power, and maintenance costs; Poor outlet temperature control.
b. Fin Fan Cooler with Dry Air Cooling in Front and Wet Air Cooling in Back
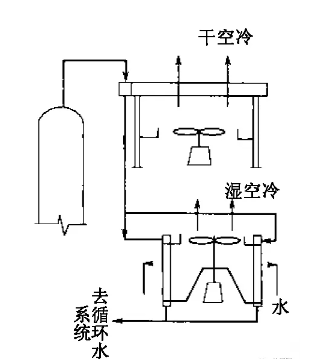
Applications and Features: Water shortages; Minimum circulating water volume required; Medium outlet temperature can be cooled to approximately 5°C above the atmospheric wet-bulb temperature; Operating costs are lower than those using water-based post-cooling; Wet air drainage can be filtered and reused, eliminating the need for a separate circulating water station or supplemental water for other circulating water systems.
Disadvantages: Post-wet air cooling occupies a slightly larger footprint than post-water cooling; Operating skills required are slightly higher than post-water cooling.
c. Combined wet-dry air cooling Fin Fan Cooler

Applications and Features: Suitable for medium to small processing capacity applications, large processing capacity applications, or applications requiring dry air cooling for large processing capacity; small footprint; low operating costs.
Disadvantages: Slightly more technically demanding than post-water cooling.
d. Fully Dry Air Cooling
Can be used in cold regions or where the media outlet temperature is 15-20°C higher than the summer design air temperature; can be used in high-pressure media cooling systems; operating costs are lower than pre-air cooling followed by post-water cooling.
e. Fully Wet Air Cooling
Applicable Applications and Features: Supplementary to dry air cooling; cooling imported media with a low temperature, and the final cooling temperature must be 5°C above the atmospheric wet-bulb temperature.
Fin Fan Cooler by Structure
1. Horizontal Structure (Induced Draft Fin Fan Cooler and Forced Draft Fin Fan Cooler)
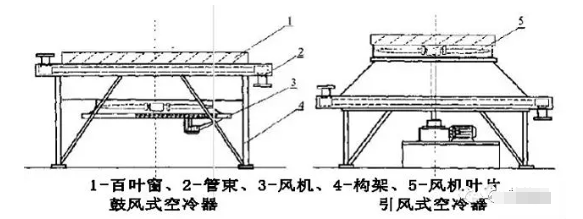
Applicable Applications and Features: Suitable for all applications. The tube bundle is placed horizontally, with a 3° or 1% inclination to prevent condensate from accumulating in the tubes.
Advantages: Simple structure, easy installation, and relatively uniform distribution of hot fluid inside the tubes and air outside.
Disadvantages: Requires a relatively large footprint, and has greater flow resistance inside the tubes than with a sloping roof type.
2. Vertical Fin Fan Cooler
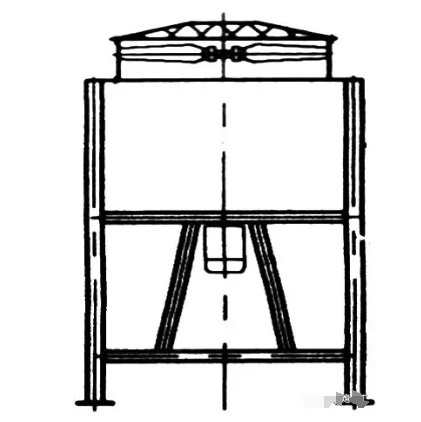
Applicable Applications and Features: The tube bundle and fan impeller are placed horizontally, with airflow perpendicular to the ground, either from bottom to top or vice versa. The structure is simple and easy to install. The condensing tube bank itself or the last stage of the tube often has a slope to facilitate drainage.
Disadvantages: It occupies a large area and has greater internal tube resistance than other types.
3. Sloped Top Fin Fan Cooler

Applications and Features: Typically used for in-tube condensation or where floor space is limited.
Advantages: Relatively uniform distribution of heat fluid within the tube and air outside. Slightly higher heat transfer coefficient than horizontal type. Low flow resistance within the tube. Small footprint.
Disadvantages: Slightly complex structure.
